Adaptive Multi-Zone IoT Security Framework for Smart Factory Systems
By Anikait Panigrahi, Barshan Mondal, and Krishnan V Namboothiri
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri Campus
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the integration of IoT technologies in smart factories has become crucial for achieving Industry 4.0 standards. This project implements a comprehensive smart factory network simulation using Cisco Packet Tracer, integrating advanced wireless technologies and IoT/IoE solutions for industrial environments.
Architecture Overview
Three-Layer Architecture
Our framework follows a robust three-layer architecture designed for scalability and reliability:
Infrastructure Layer
├── Core network backbone
├── Wireless routers and switches
└── Central servers
Communication Layer
├── Wi-Fi 6 for high-speed data
├── Mesh networking for redundancy
└── Private LTE for critical operations
Application Layer
├── IoT sensors and actuators
├── Edge computing nodes
└── User interfaces
 Three-layer architecture of the smart factory IoT security framework.
Three-layer architecture of the smart factory IoT security framework.
Key Features
- Advanced Wireless Technologies: Wi-Fi 6, mesh networking, and private LTE implementation
- Comprehensive IoT Integration: Sensors, actuators, and controllers for real-time monitoring
- Multi-Protocol Support: MQTT, Zigbee, HTTP/HTTPS protocols
- Edge Computing: Local data processing for reduced latency
- Predictive Maintenance: Real-time analytics for equipment optimization
- Scalable Architecture: Modular design supporting gradual deployment
Technical Implementation
Network Infrastructure Setup
1. Core Network Configuration
- Deploy wireless routers and managed switches
- Configure DHCP services for automatic IP assignment
- Implement VLAN segmentation for traffic isolation
2. Server Configuration
- Set up MQTT broker for IoT device communication
- Install Node-RED for visual programming and workflow automation
- Configure database servers for historical and real-time data storage
3. IoT Device Deployment
- Deploy sensors for temperature, pressure, vibration monitoring
- Configure actuators with safety interlocks
- Establish edge computing nodes for local data processing
Protocol Implementation
- MQTT: Lightweight messaging for IoT device communication
- Zigbee: Low-power mesh networking for sensor networks
- HTTP/HTTPS: Web-based interfaces and administrative functions
Wireless Solutions
- Wi-Fi 6: High-speed, low-latency connectivity for multiple simultaneous devices
- Mesh Networking: Redundant connectivity paths eliminating dead zones
- Private LTE: Dedicated wireless infrastructure for critical manufacturing processes
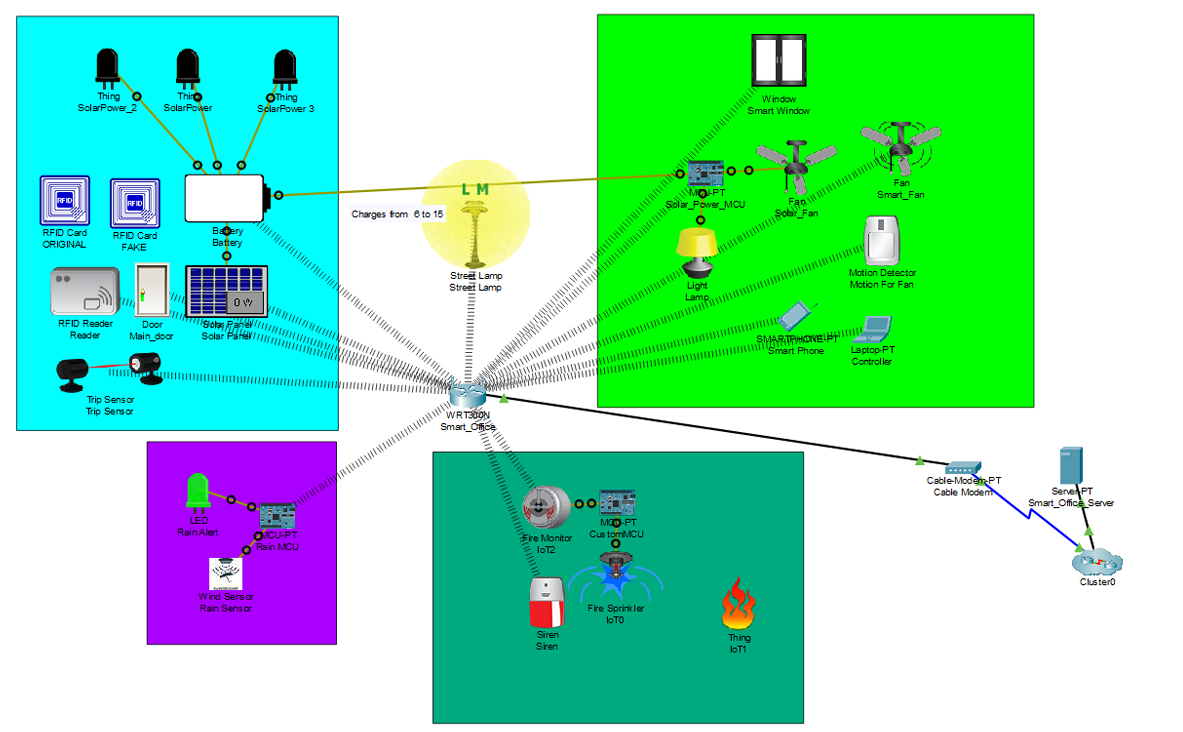 Network topology showing wireless connectivity and IoT device deployment.
Network topology showing wireless connectivity and IoT device deployment.
Performance Metrics
Network Performance
- Latency: <10ms for real-time control applications
- Throughput: Supports multiple concurrent IoT data streams
- Coverage: Complete signal coverage across factory floor
- Reliability: 99.9% uptime with redundant connectivity
IoT Device Performance
- Data Accuracy: Within acceptable tolerance ranges
- Response Time: Real-time control loop requirements met
- Energy Efficiency: Optimized power consumption for battery-powered devices
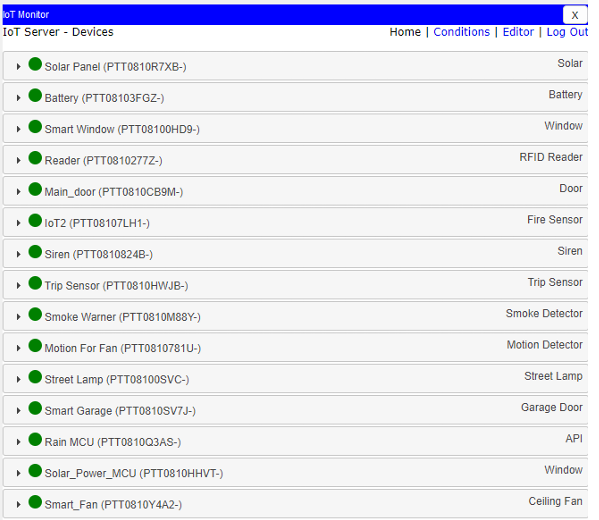
 Real-time performance metrics showing latency, throughput, and device status.
Real-time performance metrics showing latency, throughput, and device status.
Testing and Validation
Testing Procedures
- Functional Testing: Verify all system components operate per specifications
- Integration Testing: Ensure interoperability between different protocols
- Performance Testing: Evaluate system behavior under various load conditions
- Security Testing: Validate wireless authentication and data encryption
Validation Results
- Real-time data collection and processing
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Network performance meets Industry 4.0 requirements
- Complete wireless coverage validation
- IoT device integration verification
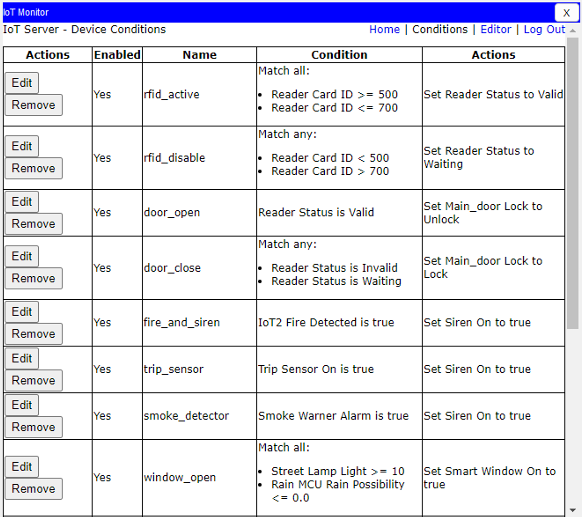
 Server configuration and IoT monitoring dashboard showing system validation and performance benchmarks.
Server configuration and IoT monitoring dashboard showing system validation and performance benchmarks.
Security Framework
Multi-Zone Security Implementation
Our adaptive security framework implements a sophisticated multi-zone approach:
- VLAN Segmentation: Network divided into security zones
- Zone-Based Access Control: Different security levels per zone
- Threat Isolation: Compromised zones isolated automatically
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuous security assessment
Security Features
- Adaptive Security: Security policies change based on zone and threat level
- Real-time Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring for security breaches
- Automatic Response: Immediate isolation of compromised devices
- Multi-Protocol Security: Security across MQTT, Zigbee, and HTTP/HTTPS
Benefits
- Real-time Monitoring: Immediate response to production anomalies
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduced unplanned downtime
- Scalable Deployment: Gradual implementation based on resources
- Enhanced Visibility: Comprehensive production process insights
- Cost Efficiency: Wireless connectivity reduces cabling requirements
Future Enhancements
- Advanced security implementations
- 5G technology integration
- Machine learning algorithms for enhanced predictive analytics
- Extended IoT device library support
- Cloud integration capabilities
Project Structure
smart-factory-iot-security/
├── simulations/
│ ├── smart-factory-network.pkt
│ ├── iot-device-configs/
│ └── network-topologies/
├── documentation/
│ ├── network-design.md
│ ├── protocol-analysis.md
│ └── performance-reports/
├── scripts/
│ ├── device-configuration/
│ └── monitoring-tools/
└── README.md
⚙️ Technical Requirements
Prerequisites
- Cisco Packet Tracer (Latest Version)
- Basic networking knowledge
- Understanding of IoT protocols
Hardware Requirements
- Wireless routers supporting Wi-Fi 6
- Managed switches with VLAN capabilities
- IoT sensors and actuators
- Edge computing nodes
- Central servers for data processing
Software Requirements
- MQTT broker implementation
- Node-RED for workflow automation
- Database management system
- Security monitoring tools
- Network management software
Key Takeaways
This project demonstrates the power of integrating multiple wireless technologies and IoT protocols in a unified smart factory environment. The adaptive multi-zone security framework ensures robust protection while maintaining operational efficiency.
The combination of Wi-Fi 6, mesh networking, and private LTE creates a resilient communication infrastructure that can handle the demanding requirements of modern manufacturing processes.
Key Insight: The fusion of multiple wireless technologies with adaptive security creates a more robust smart factory system than any single approach alone.
Contact Information
- Anikait Panigrahi: anikait05@gmail.com
- Barshan Mondal: barshan2004@gmail.com
- Krishnan V Namboothiri: krishnanvezhaofficial@gmail.com
This project is licensed under the MIT License.